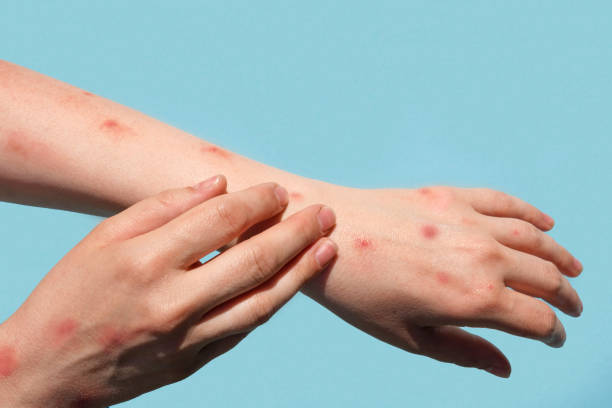
Itchy skin rashes are a common yet frustrating issue that affects millions of Americans each year. From allergies and eczema to infections and chronic conditions, the causes are wide-ranging, but proper diagnosis is key to effective relief.
This article explains the most common reasons for skin rashes that itch, how to treat them, and when it’s time to see a dermatologist.
According to the American Academy of Dermatology (AAD), 1 in 3 Americans is affected by a skin disease each year, with itching being one of the most common symptoms reported. While some rashes may resolve on their own, others can signal deeper health concerns that require medical attention.
What Are Skin Rashes That Itch?
A skin rash that itches is a noticeable change in the color, texture, or appearance of the skin, often accompanied by an uncontrollable urge to scratch.
Itching, also known as pruritus, is the body’s response to irritation or inflammation. While some rashes are temporary and harmless, others may indicate a more serious condition that requires medical attention.
Click here to learn more about the trigger warnings for Mysterious Skin.
Common Causes of Itchy Skin Rashes
According to Best Practice & Research: Clinical Rheumatology, the following are the common causes of itchy skin rashes:
1. Allergic Reactions (Contact Dermatitis)
Exposure to allergens such as poison ivy, nickel, certain fabrics, or fragrances can trigger an itchy rash. This type of dermatitis usually appears within hours to days after contact and may present as red, blistered, or dry patches.
2. Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis)
Eczema is a chronic condition often beginning in childhood and characterized by dry, scaly, and itchy skin. It tends to flare up periodically and is influenced by both genetic and environmental factors.
The National Eczema Association notes that stress, weather changes, and allergens can all contribute to flare-ups.
Click here to learn more about how to keep your skin healthy and glowing.
3. Psoriasis
This autoimmune condition causes rapid skin cell turnover, leading to thickened, scaly patches that may itch or burn. Though psoriasis is less commonly associated with severe itching than eczema, the discomfort can still be considerable.
4. Heat Rash (Miliaria)
When sweat glands become blocked, it can result in small, itchy red bumps, particularly in hot or humid conditions. This is more common in babies but can affect adults, especially during physical activity.
Click here to learn more about how to use olive oil on your face if you have oily skin.
Fungal Infections (Ringworm, Candidiasis)
Caused by an overgrowth of yeast or dermatophytes, fungal rashes are typically circular, itchy, and may spread quickly without treatment.
6. Hives (Urticaria)
These are raised, red, itchy welts on the skin that often result from allergic reactions, stress, or unknown triggers. They usually go away within hours, but may recur frequently.
Click here to learn more about the benefits of lemon juice for your skin.
7. Insect Bites
Bites from mosquitoes, bed bugs, or fleas often cause localized red, itchy bumps. In some cases, scratching can lead to infection.
Diagnosis and Tests
To properly diagnose skin rashes that itch, a dermatologist may:
- Perform a physical examination of the affected area
- Review your personal and family medical history
- Conduct patch testing for allergens
- Use a skin biopsy if a more serious condition is suspected
According to the American Academy of Dermatology, patch testing is particularly useful for identifying contact dermatitis triggers, while biopsies help differentiate between conditions that look similar but require different treatments.
Click here to learn more about how to make vitamin E oil for your skin.
Treatment Options
The treatment for itchy skin rashes depends on the underlying cause:
- Topical Steroids: Commonly prescribed for eczema, allergic reactions, and other inflammatory conditions. Hydrocortisone is widely used for mild rashes, while stronger corticosteroids may be necessary for severe cases.
- Antihistamines: These are effective in controlling allergic itching and hives.
- Antibiotic or Antifungal Creams: Used when the rash is due to infection.
- Moisturizers: Essential for managing dry and itchy skin, especially with eczema.
- Phototherapy: Sometimes used for chronic conditions like psoriasis.
- Lifestyle Changes: Reducing stress, avoiding known irritants, and using fragrance-free products can prevent flare-ups.
A study published in The Journal of Investigative Dermatology highlighted the role of the skin microbiome in eczema, suggesting that restoring healthy bacterial balance may improve symptoms, a growing area of research in dermatology.
Click here to learn more about the best hair, skin, and nail vitamins.
When to See a Dermatologist
While many itchy rashes can be treated at home, certain signs indicate it’s time to seek professional help:
- Rash persists for more than two weeks
- Severe itching disrupts sleep or daily activities
- Rash is spreading or getting worse
- Blistering, oozing, or signs of infection develop
- Over-the-counter treatments aren’t working
- You have a weakened immune system
Ignoring a persistent rash can delay the diagnosis of serious conditions like autoimmune diseases or skin cancers.
Click here to learn more about why some people’s veins appear through their skin.
What to Expect at the Dermatologist’s Office
During your appointment, the dermatologist will likely ask:
- When did the rash first appear?
- Have you recently changed skincare products, detergents, or medications?
- Is there a family history of skin conditions like eczema or psoriasis?
- Do you have other symptoms, such as fever or fatigue?
- Have you traveled recently or spent time outdoors?
These questions help narrow down possible causes and determine whether the rash is isolated or part of a systemic issue.
Click here to learn more about how both skin and lung cancer are classified as carcinomas.
A Word from GetMe Treated
Dealing with skin rashes that itch can be frustrating, but understanding the cause is key to finding relief. Whether it’s an allergic reaction, chronic condition, or an infection, there are effective treatments available.
Never ignore a persistent or worsening rash; early intervention can prevent complications and improve outcomes.
If you’re unsure about the cause or treatment of your rash, don’t hesitate to consult a board-certified dermatologist. They can provide a thorough diagnosis, offer personalized care, and help you get your skin and your comfort back on track.
Click here to learn more about how to use turmeric to brighten skin with Rongdhono.
FAQs About Skin Rashes That Itch
Can stress cause itchy skin rashes?
Yes, stress is a well-known trigger for conditions like eczema and hives. Managing stress through relaxation techniques can help reduce flare-ups.
Are all itchy rashes contagious?
No, not all rashes are contagious. Fungal infections and scabies can spread, but eczema and psoriasis are not.
Is it okay to scratch an itchy rash?
Scratching can worsen inflammation, cause skin damage, and even lead to infection. Try cold compresses or anti-itch creams instead.
Can diet affect itchy skin conditions?
Yes. Certain foods may trigger allergic reactions or inflammation. Some people with eczema find relief by avoiding dairy, gluten, or processed foods.
What’s the best soap for itchy skin?
Fragrance-free, hypoallergenic soaps are best. Avoid harsh cleansers and opt for moisturizing body washes.
How long does it take for an itchy rash to go away?
It depends on the cause. Minor rashes may clear in a few days, while chronic conditions like eczema may require ongoing management.